PON (Passive Optical Network) refers to a fiber optic network that utilizes point-to-multipoint topology and fiber optic splitters to transmit data from a single transmission point to multiple user endpoints. Unlike AON, where multiple customers are connected to a single transceiver via a fiber optic branch tree and passive splitter/combiner units, it operates entirely in the optical domain, with no power in the PON architecture. There are currently two main PON standards: Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) and Ethernet Passive Optical Network (EPON).
PON structure and components
An EPON (GEPON) system with an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and a number of Optical Network Units (ONUs) or Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) close to the end users at the service provider's central office, and optical splitters (SPL class). In addition, the optical distribution network (ODN) is also used for the transmission between OLT and ONU/ONT.
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
OLT Meaning OLT is the abbreviation of Optical Line Terminal, which is a device used to connect optical fibers and transmit signals. The OLT is the starting point of the PON, connected to the aggregation switch through Ethernet cables. It makes a significant difference in PON. OLT equipment components OLT equipment generally includes racks, CSM (Control and Switch Module), ELM (EPON Link Module, PON card), redundant protection-48V DC power supply module or a 110/220V AC power supply module, and fans. In these sections, PON cards and power supplies are hot-swappable, while another module is built in. OLT has two floating directions: uplink (get different types of data and voice traffic from users) and downlink (get data, voice and video traffic from metro network or long-distance network and send to all ONT modules on ODN.) OLT Functional OLT equipment is an important central office equipment in EPON. It is a multi-service providing platform that supports both IP services and traditional TDM services. Placed at the edge of the MAN or at the exit of the community access network, the access services are aggregated and transmitted to the IP network respectively. EPON passive optical network system has flexibility. Connect multiple terminals of service access points within a radius of 20 kilometers to form an EPON system network. The system can support a variety of business models, adapt to a variety of working environments, and provide users with FTTx series solutions. In addition to providing service aggregation functions, the OLT is also a centralized network management platform. The OLT can implement device-based network element management and service-based security management and configuration management. It can not only monitor and manage devices and ports, but also perform service provisioning and user status monitoring, and allocate bandwidth according to the QoS/SLA requirements of different users.
Send Ethernet data to ONU in broadcast mode;
Initiate and control the ranging process, record ranging information;
Allocate bandwidth for ONU; that is, control the start time of ONU sending data and the size of the sending window.
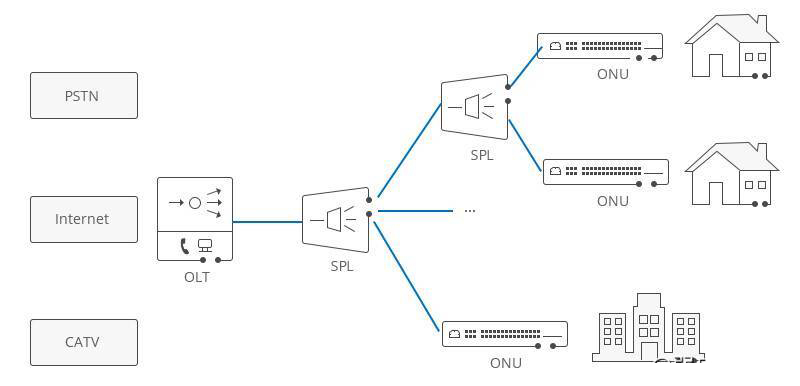
OLT uses OLT equipment to cooperate with different types of ONUs to realize various access networks such as FTTC, FTTH, FTTO, and FTTM. On the one hand, the signals carrying various services are aggregated at the central office and sent to end users to access the network according to a certain signal format; On the other hand, signals from end users are sent to different service networks according to different service types. The figure below is FTTH (Fiber to the Home) application. The OLT is connected to the management switch and the ONU. There is a splitter between OLT and ONU. The entire PON can provide multiple services such as IPTV, VOIP, and IP Camera for multiple families.
Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking
Optical Network Unit (ONU) / Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
The ONU converts optical signals transmitted through optical fibers into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then sent to individual users. Typically, there is a distance or other access network between the ONU and the end user premises. In addition, ONU can send, aggregate and organize different types of data from customers and send it upstream to OLT. Marshalling is the process of optimizing and reorganizing the flow of data for more efficient delivery. The OLT supports bandwidth allocation, which allows smooth transfer of data floats to the OLT, which usually arrive from the customer in bursts. ONUs can be connected in a variety of ways and cable types, such as twisted-pair copper wire, coaxial cable, fiber optics, or via Wi-Fi. End-user equipment may also be referred to as an optical network terminal (ONT). In fact, ONT is essentially the same as ONU. ONT is an ITU-T term and ONU is an IEEE term. Belonging to different standard bodies, they all refer to the user-side equipment in the EPON system. However, in practical applications, there is still a little difference between ONT and ONU according to different locations.
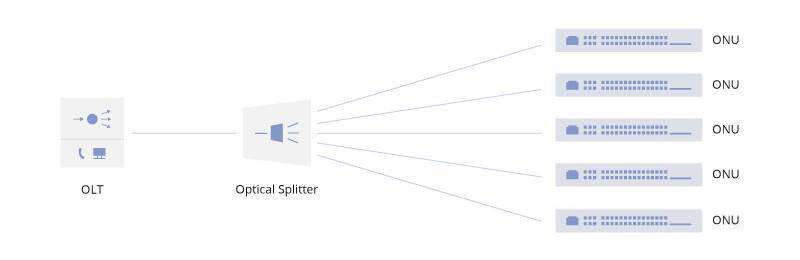
Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking
Optical Distribution Network (ODN)
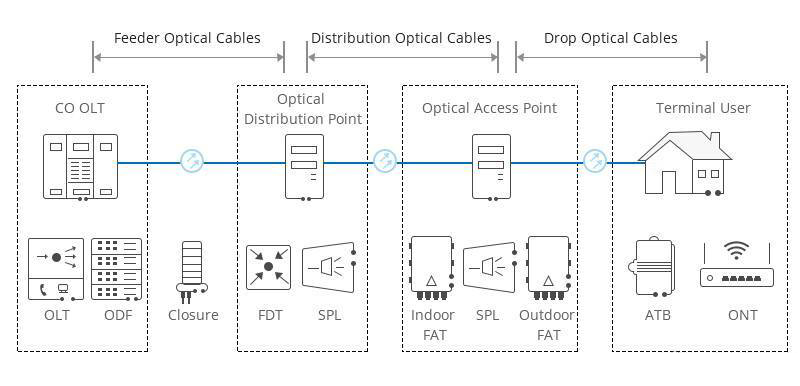
ODN is an integral part of the PON system, which provides an optical transmission medium for the physical connection from ONU to OLT, and the distance can reach 20 kilometers or more. In ODN, optical cables, optical connectors, passive optical splitters and auxiliary components cooperate with each other. ODN is specifically divided into five parts: feeder fiber, optical distribution point, distribution fiber, optical access point, and fiber entry. The feeder fiber starts from the optical distribution frame (ODF) in the central office and ends at the optical distribution point for long-distance coverage. The distribution fiber from the optical distribution point to the optical access point distributes the fiber for the area next to it. The incoming fiber connects the optical access point to the terminal (ONT) to realize fiber-to-the-home. In addition, ODN is an essential channel for PON data transmission, and its quality directly affects the performance, reliability and scalability of the PON system.
Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking Detailed explanation of OLT, ONU, ONT and ODN in PON networking
in conclusion
OLT, ONU or ONT, ODN are the main components in the GEPON system, and are widely used in FTTH applications at present. Reduced wiring infrastructure (no active components) and flexible media transport make PON more suitable for home Internet, voice and video applications. In addition, passive optical networks can also be applied to university campuses and commercial environments, providing cost-effective solutions. As PON technology continues to improve, the potential applications continue to expand.


 CIOE2023: Pioneering the Future of Intelligent Communication with eNet
CIOE2023: Pioneering the Future of Intelligent Communication with eNet
 eNet GPON OLT Basics and Configuration
eNet GPON OLT Basics and Configuration
 What is FTTH? How Does it Work?
What is FTTH? How Does it Work?
 Application of Optical Transceiver Module in OLT
Application of Optical Transceiver Module in OLT